 Paro Taktsang (Dzongkha: སྤ་གྲོ་སྟག་ཚང་, also known as the Taktsang Palphug Monastery and the Tiger's Nest)
Paro Taktsang (Dzongkha: སྤ་གྲོ་སྟག་ཚང་, also known as the Taktsang Palphug Monastery and the Tiger's Nest) Member Since 1973
Partner Ministry/Organization Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Ministry of Labor and Human Resource (MoLHR) Recent Programs Held 2019: (1) The Role of Accreditation in Achieving Quality-Assured TVET Programs (Apr 1-5) 2018: (1) Consultative meetings of officials from the Department of Technical Education (DTE), Ministry of Labour and Human Resources (MoLHR) Kingdom of Bhutan (Dec 15-28); (2) Consultative meetings of officials from the Ministry of Labor and Human Resources (MoLHR) and the National Environmental Commission (NEC) (Apr 25-29) 2017: In-Country Program on National Diploma Curriculum Development and Training of Trainers in Pedagogy (Jun 5-17) 2016: In-Country Program on TVET Pathways to Sustainable Development (Oct 17-21) 2015: In-Country Program and National Seminar on Entrepreneurship Education (Oct 5-9) 2014: In-Country Program on Image-Building of TVET (Oct 7-11) 2013: In-Country Program on Developing Generic Skills for Employment Mobility (Oct 7-11) 2012: Special In-Country Program on Developing Champion Leaders for Skills Development for Poverty Alleviation (Aug 22-25) 2011: In-Country Program on Total Quality Management for TVET (Apr 5-9) Address of Embassy/Consulate in Manila N/A |

Official Name
Kingdom of Bhutan
Land Area
38,394 km2 (14,824 sq mi) (136th)
Population
779,898 (165th)
Capital
Thimphu (est. pop. 98,676)
Largest Cities
Punakha (est. pop. 21,500)
Tsirang (est. pop. 18,667)
Phuntsholing (est. pop. 17,043)
Pemagatshel (est. pop. 13,864)
Tsirang (est. pop. 18,667)
Phuntsholing (est. pop. 17,043)
Pemagatshel (est. pop. 13,864)
Country Borders
China (north,eest), India (south, west)
Religion/s
Buddhism
Major Language/s
Dzongkha
Demonym
Bhutanese
National Holidays
17 December 1919 (coronation of Ugyen Wangchuck as the first Druk Gyalpo of modern Bhutan)
Education Basic Facts
No. of Years of Primary Education
12
Major University
University of Bhutan
Primary School Enrollment (Total)
105.81% (UNESCO, 2020)
Tertiary School Enrollment (Total)
116.4% (UNESCO, 2020)
Ministry/ Ministries Supervising Education
Ministry of Education, Department of Adult and Higher Education
Education as % of GDP
6.9 % (UNESCO, 2018)
TVET
Agency Handling TVET
Ministry of Labour and Human Resources (MoLHR)
Formal TVET system
TVET is offered at the secondary education level. At the middle secondary education level, students are able to take pre-vocational subjects provided according to local needs and the availability of equipment, local traditions, indigenous knowledge and skills. Students are required to pass an examination to attend general upper secondary or vocational and technical education. The duration of TVET programs varies from six months to two years and the subjects are linked to the needs of the Bhutanese labor market and economy. Specifically elective courses focus on providing skills for the development of the following key industries:
- Infrastructure: hydrogenation, power transmission and distribution, construction;
- Services: tourism, healthcare, education, information technology (IT), financial services;
- Manufacturing: cement, herbal products; and
- Royal Civil Service Commission (government).
In addition to TVET programs offered at the upper secondary education level, the Institute of Zorigchusum Thimphu and Institute of Zorigchusum Tashiyangste vocational training institutes also offer long TVET programs lasting up to six years, in wood carving, painting and tailoring.
TVET at the tertiary level is offered through institutions accredited to the Royal University of Bhutan and providers registered with the Department of Occupational Standards. TVET programs can be part-time or full-time and are conducted in a number of colleges and vocational institutes. Most TVET programs last four years and focus on engineering, technology, business administration, and education. Medicine programs last five years.
Non-formal and informal TVET systems
Non-formal, or alternative modes of TVET in Bhutan includes the following:
Apprentice training programs are provided through a contract between an apprentice and an employer. Training periods normally last six to nine months, and in some cases one year, and aim to provide students with appropriate skills and competencies for the world of work. The apprentice training program covers all sectors, but mostly concentrates on the service and hospitality sector;
Special skills development programs are geared towards the training of armed forces and special needs groups in vocational skills. Some examples of organizations providing such programs are the Dratshang Lhentshog, the Royal Bhutan Police, Draktsho, RENEW and the Royal Bhutan Army;
Village skills development programs provide skills training for villagers and aim to enhance the quality of life in the rural community, enhance community participation, and promote lifelong learning and sustainable development in the rural community. Instructors, tools and training materials are sent to villages and the training is conducted in the villages and communities themselves; and
Skills training programs aim to address the immediate human resource requirements in the labor market through skills training. Some of the skills training program initiatives include the Youth Employment Skills, Graduate Skills Program, and the Skills for Employment and Entrepreneur Development Programs.
Currently there is no information on informal TVET in the Kingdom of Bhutan.
Offers NVQS
Yes
Type of NVQS
Bhutan Vocational Qualifications Framework (BQF) serves as a point of reference for all qualifications and contains information on qualifications for various local and international stakeholders.
- Establish and maintain ANQF for the development, recognition and award of qualifications, based on knowledge, skills and competence acquired by learners;
- Establish and promote the maintenance and improvement of the standards of further education and training awards in Higher education, TVET, general education, Islamic education and Basic education; and
- Promote and facilitate access, transfer and progression within the national education system.
Levels of NVQS
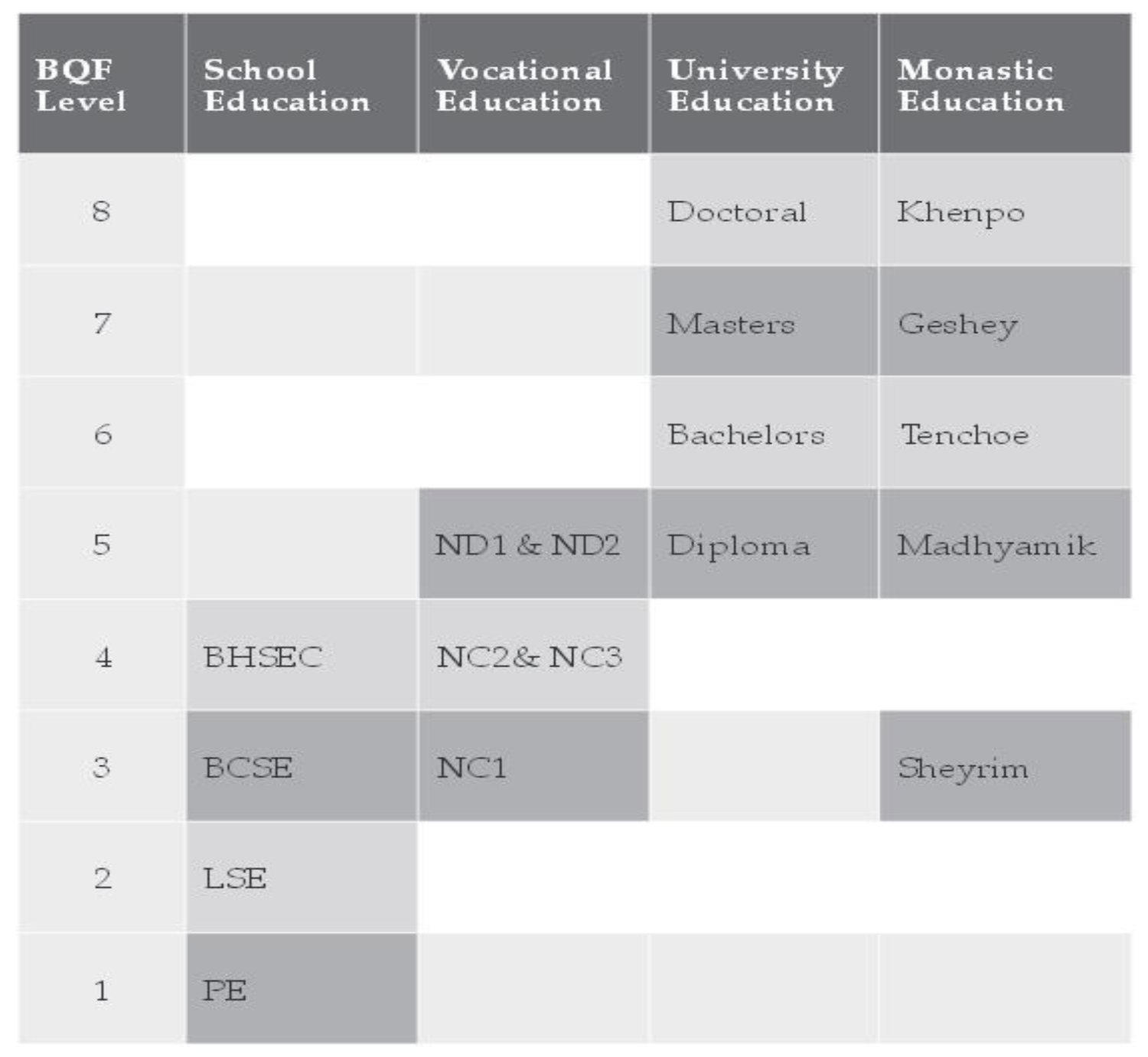
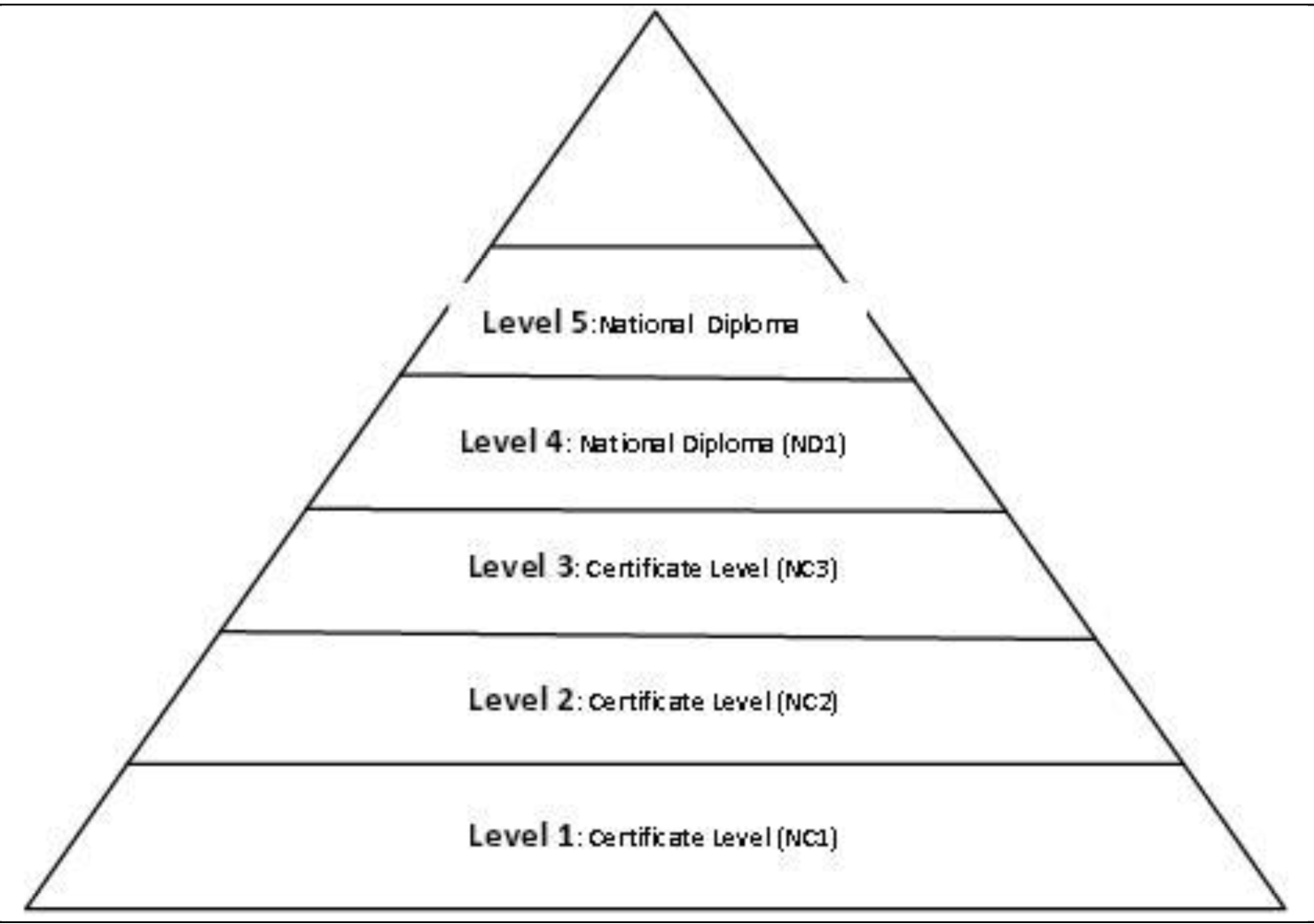
Competency Standards
TVET Financing
Formal TVET programmes offered by middle and upper secondary education level vocational education and technical training institutes are funded by the Ministry of Education and the Ministry of Labour and Human Resources. Other actors involved in financing non-formal TVET programmes include the private sector through PPP and Employee Education and Training Funds (EEFE), and other national governments.
TVET System
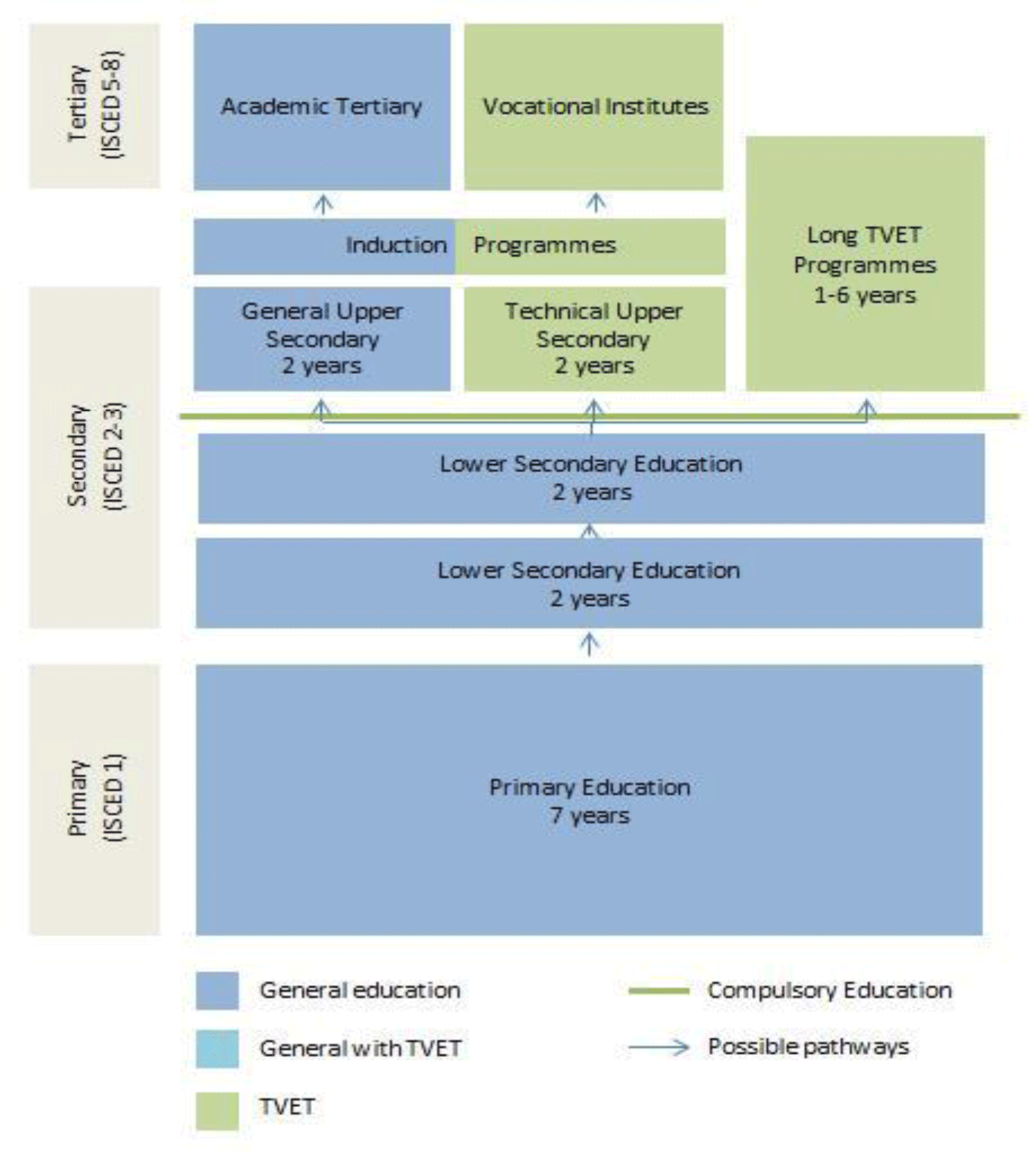
Sources:
- UNESCO-UNEVOC (2014). Bhutan. Retrieved on http://www.unevoc.unesco.org/go.php?q=World+TVET+Database&lang=en&ct=BTN
- Ministry of Education Bhutan (2019). About Us. Retrieved on: http://www.molhr.gov.bt/molhr/
- Ministry of Labor and Human Resources Bhutan (2019). About Us. Retrieved on: http://www.molhr.gov.bt/molhr/
GDP
$2,315,437.34 (2020)
GDP Per Capita
$3,000.8 (2020)
Currency
Bhutanese Ngultrum (BTN) = 100 chhertum
Major Exports
Ferroalloys (54.9% = $137M), Dolomite (10.1% = $25.3M), Semi-Finished Iron (8.87% = $22.2M), Cement (5.9% = $14.8M), and Carbides (3.9% = $9.76M)
Major Imports
Refined Petroleum (17.5% = $144M), Iron Reductions (5.7% = $46.7M), Delivery Trucks (3.73% = $30.5M), Cars (3.44% = $28.2M), and Wood Charcoal (3.04% = $24.9M)
Major Industries
Cement, wood products, processed fruits, alcoholic beverages, calcium carbide, tourism
Major Export Partners
India (93.7% = $234M), Italy (2.15% = $5.38M), Turkey (0.56% = $1.39M), Germany (0.5% = $1.26M), and Singapore (0.49% = $1.23M)
Major Import Partners
India (84.7% = $694M), Thailand (5.06% = $41.5M), France (2.35% = $19.3M), United Arab Emirates (1.45% = $11.9M), and China (1.31% = $10.7M)
Foreign Exchange Reserves
$ 1.51 billion (2020)
Ease of Doing Business Rank
89th (out of 190) (2019)
Inflation
6.9%
Population below Poverty Line
8.2% (2017)
Gini Coefficient
37.4% (2017)
Competitiveness Rank
82nd (out of 140)
Ease of Doing Business Rank
89th (out of 190) (2019)
Employment Rate
62.85% (2020)
Unemployment Rate
3.1% (2017)
 King Jigme Khesar Namgyel Wangchuck / (Paula Bronstein/Getty Images)
King Jigme Khesar Namgyel Wangchuck / (Paula Bronstein/Getty Images)
Type of Government
Unitary parliamentary constitutional monarchy
Head of State
King Jigme Khesar Namgyel Wangchuck
Head of Government
Tshering Tobgay
Legislating Body/Bodies
- Parliament of Bhutan (Gyelyong Tsokhang)
- Upper House: National Council
- Lower House: National Assembly
 BOISVIEUX Christophe via Getty Images
BOISVIEUX Christophe via Getty Images
Time zone
UTC +6:00
Human Development Index
0.654 (md, 129th out of 189) (2019)
Literacy Rate
66.6% of the total population (Male: 75%; Female: 57.1%) as of 2017
% of people with internet access
48.1% (approx. 373.2 thousand of the population) (Kemp, 2021)
Life Expectancy
Total: 71 years (Male: 71 years; Female: 72 years) (2019)
Doctors per Capita
0.46 Physicians; and 1.829 nurses & midwives per 1,000 population (2019)
Drives on the
Left
Calling code
+975
ISO 3166 code
BT
Internet TLD
.bt








